19 Historical Events That Changed The Way We Live Today
The fabric of our current lives is woven with threads from the past, with each historical event contributing to the complex tapestry of human existence. The following 19 historical events have had profound impacts on society, culture, technology, and governance, shaping the way we live today in ways both big and small.
The Invention of the Wheel (circa 3500 BC)

Credit: Facebook
Revolutionizing transportation and labor, the wheel became foundational to advancements in agriculture, trade, and warfare, ultimately facilitating global exploration and connectivity.
The Writing of the Magna Carta (1215)

Credit: Reddit
This landmark document limited the power of the monarchy in England, laying the groundwork for modern democracy and emphasizing the importance of a government’s accountability to its people.
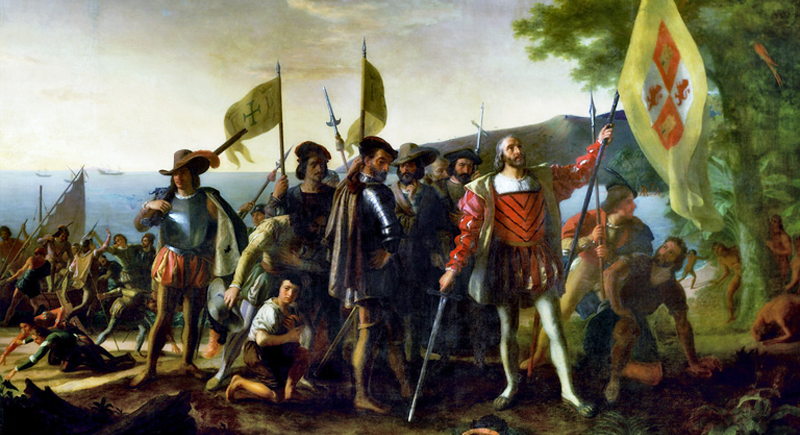
The Discovery of the Americas by Christopher Columbus (1492)

Credit: flickr
Columbus’s voyage opened the floodgates for European exploration and colonization of the Americas, reshaping the world’s geopolitical and cultural landscapes.
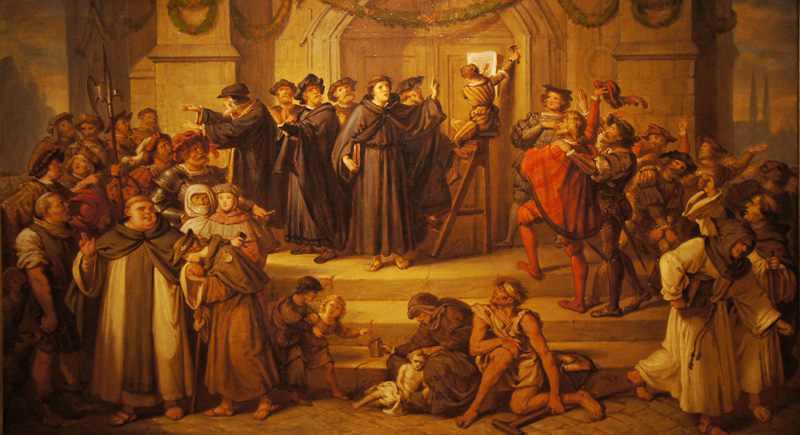
The Protestant Reformation (1517)

Credit: flickr
Initiated by Martin Luther, this religious movement profoundly affected the Christian Church, leading to the diversification of religious practices and laying early groundwork for religious freedom.
The Invention of the Printing Press by Johannes Gutenberg (circa 1440)

Credit: World History
The printing press democratized knowledge, making books and information accessible to a wider audience and fueling the Renaissance, the Scientific Revolution, and the Reformation.
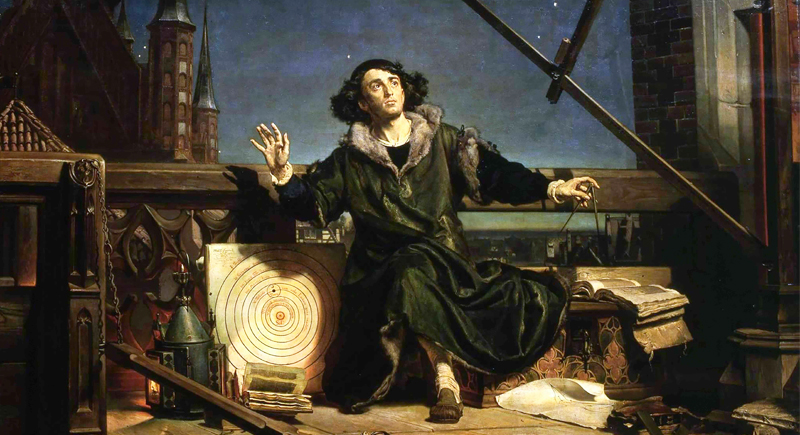
The Scientific Revolution (16th and 17th Centuries)

Credit: Wikioo
This period of advances in mathematics, physics, astronomy, biology, and chemistry transformed views of society and nature, laying the foundations of modern science.
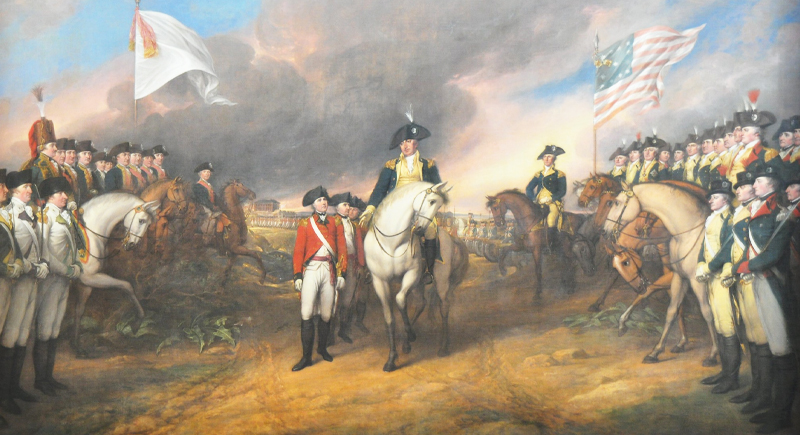
The American Revolution (1775-1783)

Credit: flickr
The successful revolt of the American colonies against British rule not only created a new nation but also inspired revolutions around the world, promoting ideas of liberty and democracy.
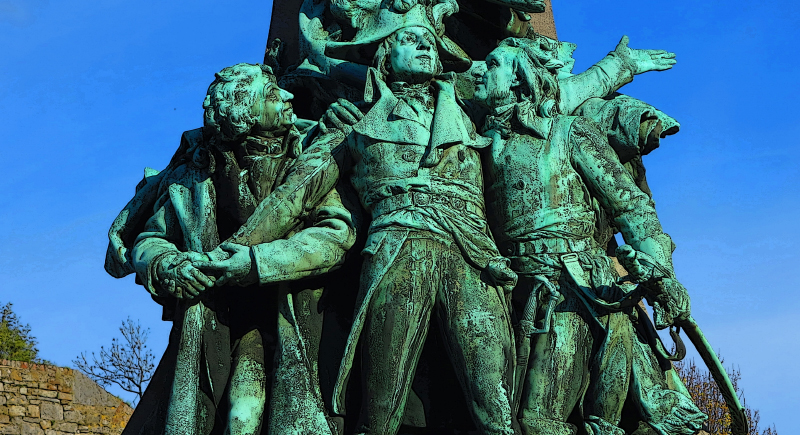
The French Revolution (1789-1799)

Credit: Wikimedia Commons
It drastically changed the social and political structure of France, leading to the rise of Napoleon Bonaparte and influencing revolutionary movements globally.
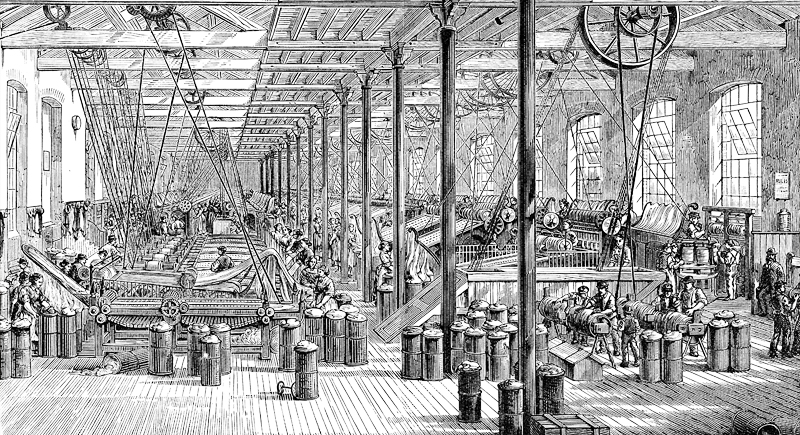
The Industrial Revolution (18th and 19th Centuries)
Credit: Wikimedia Commons
The transition to new manufacturing processes and industrialization reshaped societies, leading to urbanization, technological advancements, and significant changes in economic and labor systems.
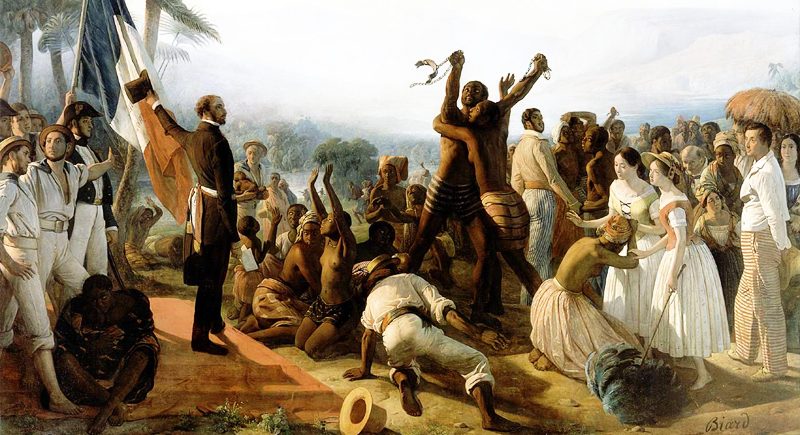
The Abolition of Slavery (19th Century)

Credit: Wikimedia Commons
Beginning in Britain (1833) and followed by the United States (1865), the abolition of slavery marked a significant moral and social turning point, impacting labor systems worldwide and advancing human rights.
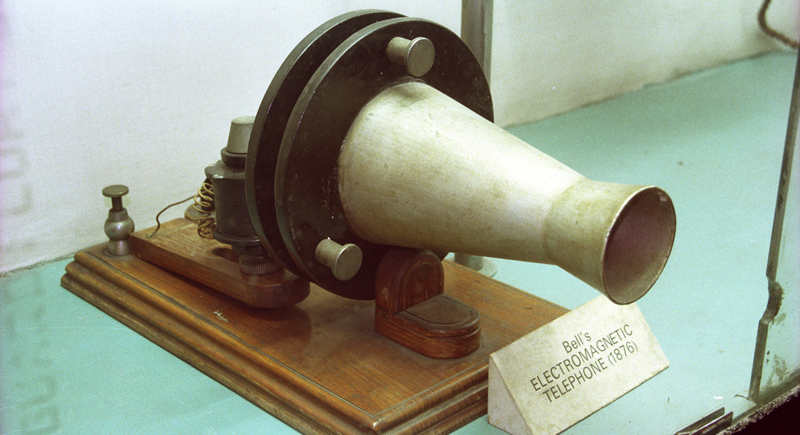
The Invention of the Telephone by Alexander Graham Bell (1876)
Credit: Wikimedia Commons
Revolutionizing communication, the telephone paved the way for the global communications network and the interconnected world we live in today.
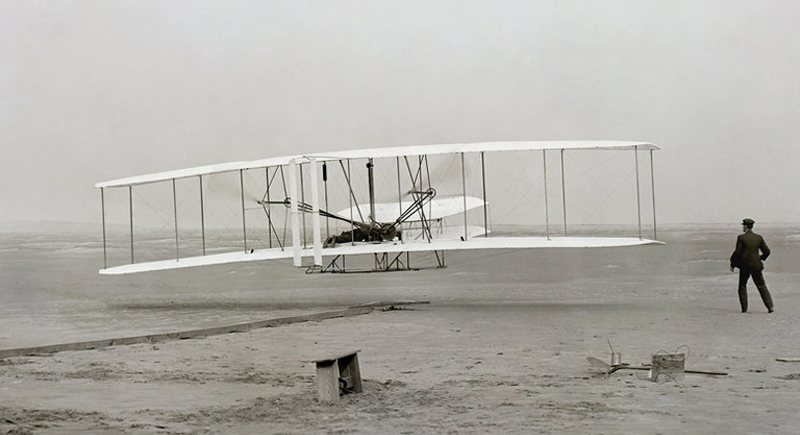
The Wright Brothers’ First Powered Flight (1903)

Credit: flickr
This breakthrough in aviation technology made long-distance travel faster and more accessible, shrinking the world and enabling global connectivity.
Women’s Suffrage Movements (Late 19th-early 20th Centuries)

Credit: flickr
The fight for women’s voting rights, culminating in various legislative changes around the world, was a crucial step toward gender equality in democratic societies.
The Russian Revolution (1917)

Credit: Wikimedia Commons
The overthrow of Russia’s monarchy and the establishment of a communist state influenced global politics and led to the Cold War, significantly shaping international relations in the 20th century.
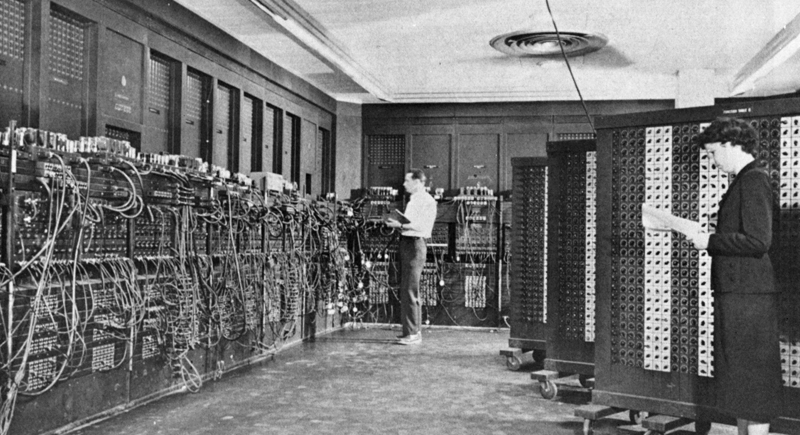
The Invention of the Internet (1960s-1980s)

Credit: Wikimedia Commons
Initially a way to share information between computers, the internet has become a global system of communication and commerce, reshaping every aspect of modern life.
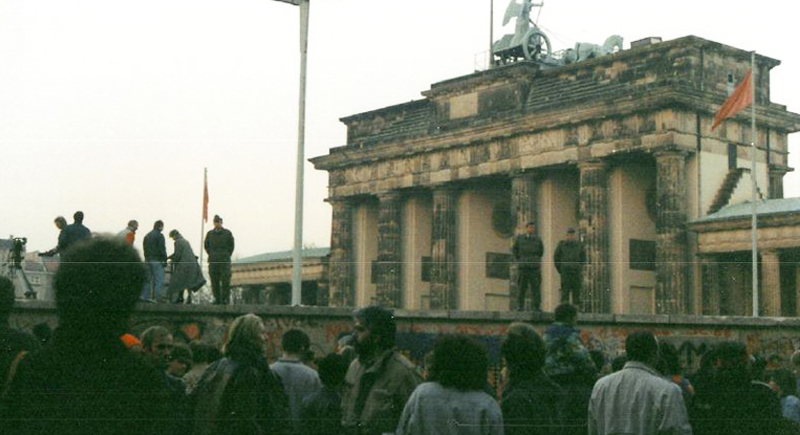
The Fall of the Berlin Wall (1989)

Credit: flickr
Symbolizing the end of the Cold War, the fall of the Berlin Wall marked the beginning of Germany’s reunification and a shift toward a new world order.
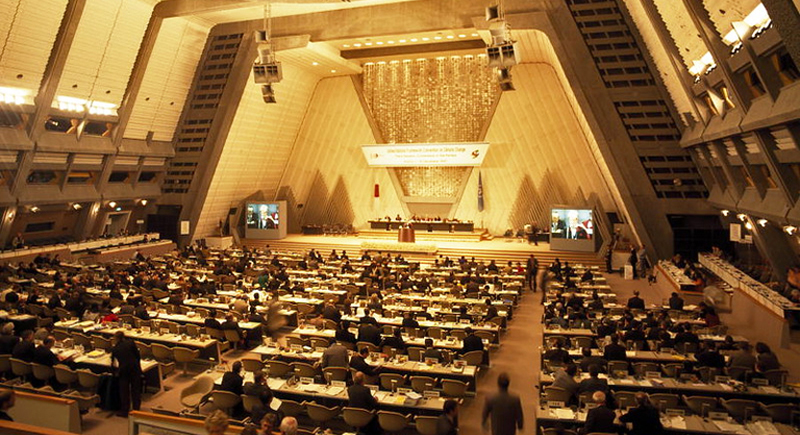
The Signing of the Kyoto Protocol (1997)

Credit: flickr
This international treaty was one of the first major global efforts to confront the challenge of climate change. Committing signatory nations to reduce greenhouse gas emissions marked a pivotal step toward influencing subsequent environmental policies and international agreements.
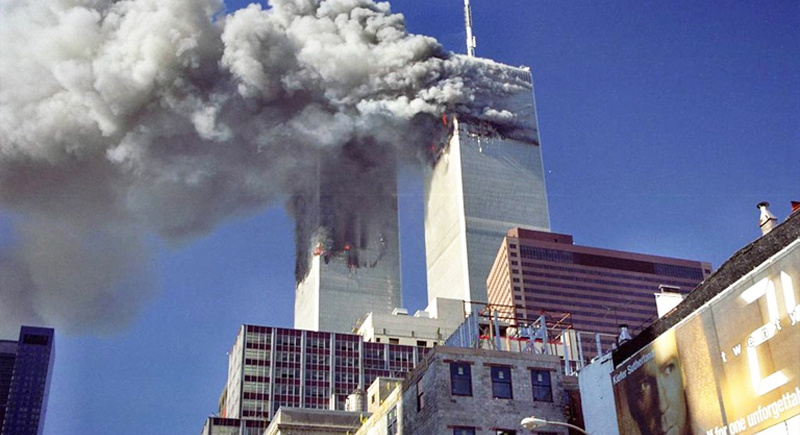
The September 11 Attacks (2001)

Credit: flickr
These terrorist attacks on the United States led to global efforts to combat terrorism, altering international law and changing national security policies worldwide.
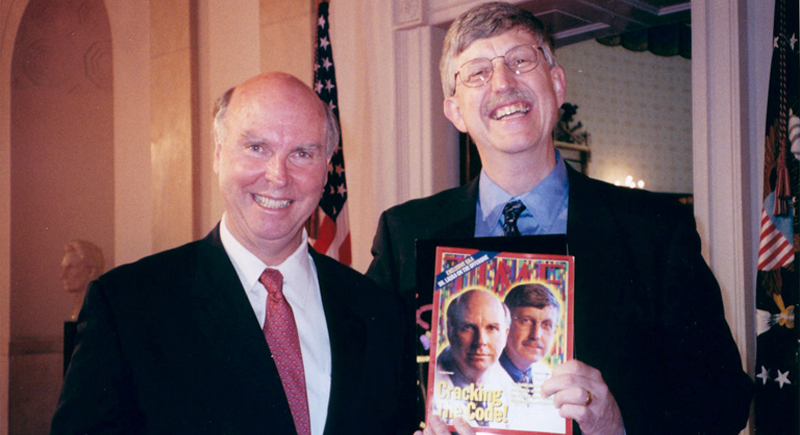
The Human Genome Project Completion (2003)

Credit: flickr
Mapping the entire human genome has vast implications for medicine, genetics, anthropology, and law, promising personalized medicine and insights into human evolution and biology.